Pulmonary Treatments in Bakersfield, Ca
Pulmonary Treatments
- Pulmonary Function Testing
- Sleep Study
- Oxygen Therapy
- Non-invasive Ventilation
- Bronchoscopy
- Bronchial Rheoplasty
- Fiducial Markers
- Thoracentesis
- Lung Cancer Diagnostics
- Lung Cancer Tumor Ablation with Argon Plasma Coagulation
- Computer-Guided Navigation Bronchoscopy
- Zephyr Intrabronchial Valve placement and Treatment
- Bronchoscopy Lung Volume Reduction
- EBUS
- Pleurx Catheter Placement and Treatment
- Pleural Effusions
- Pulmonary Emboli
- Bronchoscopic Lung Cryobiopsy
- Tracheostomy Placement
Our Pulmonary Treatments
Bronchoscopic Procedures
Bronchoscopy is a medical procedure that plays a vital role in diagnosing and treating various respiratory conditions by allowing direct visualization of the airways and lungs. During a bronchoscopy, a thin, flexible tube called a bronchoscope is inserted through the nose or mouth and gently guided down the throat and into the airways. This bronchoscope is equipped with a light source and a camera that transmit real-time images of the airways to a monitor, enabling the healthcare provider to closely examine the bronchial tubes and lungs. Additionally, specialized instruments can be passed through the bronchoscope to take tissue samples, perform biopsies, or remove foreign objects or excess mucus, all while the patient is under sedation or anesthesia to ensure comfort and minimal discomfort.
Bronchoscopy serves multiple essential purposes in the field of pulmonology. It is invaluable for diagnosing conditions such as lung cancer, chronic bronchitis, and pulmonary infections. Moreover, bronchoscopy allows for the evaluation of unexplained coughs, the assessment of airway abnormalities, and the monitoring of treatment responses in patients with lung diseases. This versatile procedure not only aids in diagnosis but also provides interventional opportunities, such as the removal of airway obstructions, the treatment of bleeding in the airways, and the placement of stents to keep airways open. Overall, bronchoscopy is a crucial tool in the arsenal of respiratory medicine, enabling healthcare professionals to offer precise diagnoses and targeted treatments for a wide range of pulmonary conditions.
EBUS
Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) is a minimally invasive but highly effective procedure to evaluate and biopsy lymph nodes located adjacent to the airways. The EBUS procedure uses a long, narrow device called a bronchoscope, which is inserted into the body via the mouth and then passes down into the airways and lungs. At the end of the bronchoscope is a camera and ultrasound probe that allow doctors to get a clear image of the inside of the trachea and breathing tubes. During an EBUS, doctors obtain tissue samples using a technique called transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS TBNA) from the lymph nodes inside the chest, a part of the body known as the mediastinum, which is then viewed under a microscope to look for the presence of cancer cells. An EBUS is a more complex procedure than a traditional bronchoscopy. It is a tool used to help diagnose and stage lung cancer and various other conditions affecting the lymph nodes, such as inflammatory conditions like sarcoidosis or infections such as pulmonary coccidioidomycosis (valley fever), tuberculosis, etc. It was developed as an alternative to mediastinoscopy since it allows for a less invasive procedure to be performed.
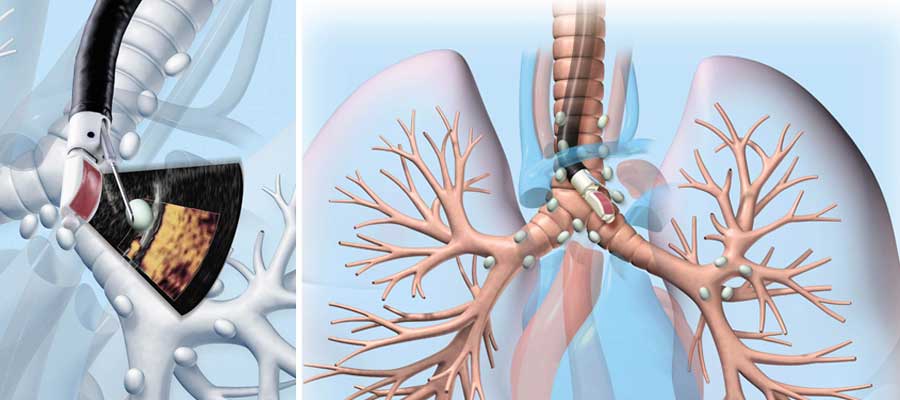
Computer-Guided Navigation Bronchoscopy
Computer-Guided Navigation Bronchoscopy, often referred to simply as Navigation Bronchoscopy, is a cutting-edge medical procedure that combines technology and expertise to revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of lung diseases. This advanced technique involves the use of specialized software and real-time imaging to navigate and access the intricate airways of the lungs. During the procedure, a bronchoscope equipped with electromagnetic sensors or other tracking technologies is carefully inserted into the patient’s airways. The computer system then generates a detailed, three-dimensional map of the lungs, providing the interventional pulmonologist with a highly accurate roadmap to target specific areas of interest, such as suspicious nodules, tumors, or sources of infection.
One of the primary advantages of Computer-Guided Navigation Bronchoscopy is its ability to reach peripheral and difficult-to-access regions of the lungs, which were traditionally challenging to diagnose or treat. This minimally invasive approach reduces the need for more invasive procedures like surgery and can lead to quicker recovery times and fewer complications for patients. Additionally, it allows for real-time biopsies and sample collection, enabling accurate and timely diagnoses. Overall, Computer-Guided Navigation Bronchoscopy is an essential tool in the field of pulmonary medicine, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of lung disease diagnosis and treatment while minimizing patient discomfort and invasiveness.
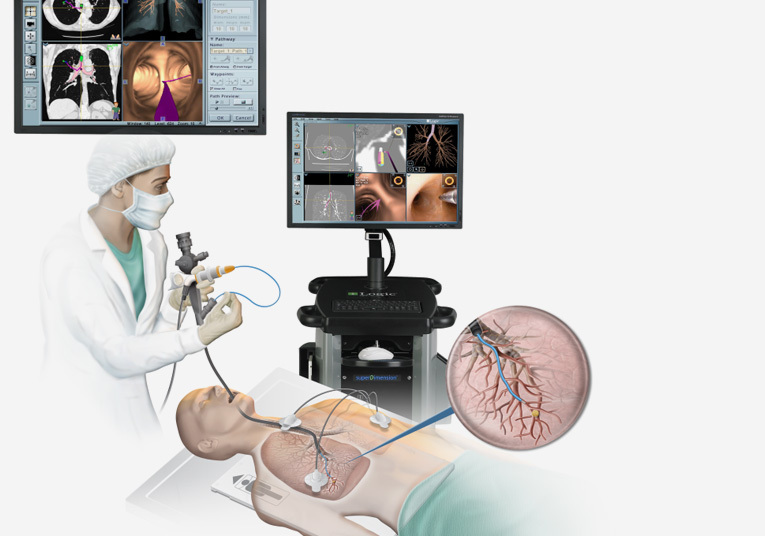
Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction / Zephyr Valve Placement
Bronchoscopy Lung Volume Reduction (BLVR) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to improve lung function and quality of life for individuals with severe emphysema, a form of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). During a BLVR procedure, a bronchoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera and small tools, is inserted into the airways through the mouth or nose. The procedure aims to reduce the volume of overinflated, damaged lung tissue, which can help alleviate the debilitating symptoms associated with emphysema, such as shortness of breath and decreased exercise capacity.
BLVR offers several advantages over traditional surgical approaches, as it is less invasive and typically involves shorter recovery times. There are different BLVR techniques available, including endobronchial valves and coils, which are strategically placed within the airways to block off or compress damaged lung areas, allowing healthier lung tissue to function more efficiently. While BLVR can be a valuable option for selected emphysema patients, it is essential to undergo a thorough evaluation and consultation with a pulmonologist or respiratory specialist to determine whether the procedure is suitable for an individual’s specific condition and to discuss potential risks and benefits.
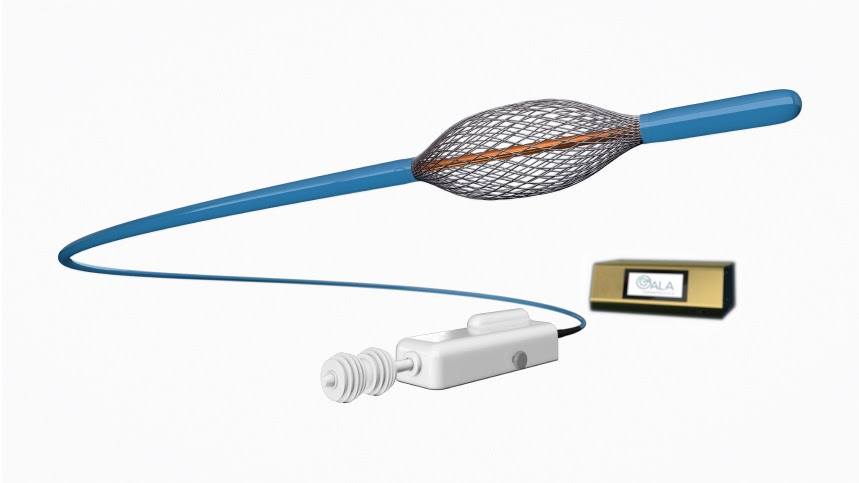
Zephyr endrabronchial Valve Placement is a minimally invasive medical procedure used in the treatment of severe emphysema, a debilitating lung condition characterized by damaged and enlarged air sacs that result in impaired lung function. The primary goal of this procedure is to provide relief and improve quality of life for individuals who have exhausted other treatment options. During the Zephyr valve placement, small, one-way valves are inserted into the airways of the lungs, specifically into the bronchial passages leading to the most affected areas. These valves work by allowing air to exit the damaged lung regions during exhalation but preventing it from re-entering during inhalation. As a result, healthier parts of the lung can function more efficiently, leading to improved breathing and exercise capacity.
The Zephyr Endobronchial Valve Placement procedure offers several advantages. It is a less invasive alternative to traditional lung surgeries, such as lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) or lung transplantation. Patients typically experience a shorter recovery time, a reduced risk of complications, and improved lung function, which can translate into increased physical activity and an overall better quality of life. While the Zephyr valve placement procedure can significantly benefit eligible emphysema patients, it’s important to note that not everyone with emphysema is a suitable candidate. Careful evaluation by a healthcare team is essential to determining eligibility and providing personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual’s specific condition and needs.

Pleurx Catheter Placement and Treatment
The Pleurx Catheter is a medical device designed to assist individuals suffering from recurrent pleural effusions, a condition characterized by an abnormal buildup of fluid in the space between the lung and the chest wall. Pleural effusions can result from various underlying medical conditions, including cancer, congestive heart failure, and infections. The Pleurx Catheter placement procedure involves a minimally invasive approach performed in a hospital or outpatient setting. Under local anesthesia and with guidance from imaging techniques like ultrasound or CT scans, a small incision is made in the chest wall, and a flexible catheter is inserted into the pleural space. The catheter is then secured in place with a stitch, and the external end is connected to a vacuum bottle or drainage bag. This catheter allows for the safe and controlled removal of excess pleural fluid, providing relief from symptoms such as shortness of breath and chest discomfort.
Once the Pleurx Catheter is in place, patients or their caregivers can be trained by healthcare professionals to perform regular drainage at home. This outpatient drainage process is relatively straightforward and involves attaching a sterile drainage bottle to the catheter, which uses a one-way valve system to ensure the flow of fluid out of the chest and into the bottle. The collected fluid can be measured and disposed of appropriately. This approach allows for convenient and painless management of pleural effusions, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits. It’s crucial for patients and their healthcare providers to work together closely to monitor and maintain the catheter, ensure sterile technique during drainage, and address any potential complications promptly. Pleurx Catheter placement and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with recurrent pleural effusions, allowing them to better manage their condition and alleviate associated symptoms.

Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis serves both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In the diagnostic context, it allows healthcare professionals to analyze the pleural fluid obtained for signs of infection, inflammation, cancer cells, or other abnormalities. On the therapeutic side, thoracentesis can provide relief for individuals experiencing symptoms such as chest pain and difficulty breathing due to the pressure caused by excess fluid or air. The procedure is typically done under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort, and real-time imaging, such as ultrasound, may be used to guide the needle placement safely. While thoracentesis is generally considered safe, it’s essential for patients to discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure, as individual circumstances may vary.

Bronchial Rheoplasty
The RheOx® system for the treatment of the symptoms of chronic bronchitis consists of a proprietary electrosurgical generator and a single-use catheter. The minimally-invasive bronchoscopic therapy delivers short bursts of non-thermal energy to the airways in the lung to reduce the abnormal mucus-producing cells, leaving the extracellular matrix intact so that the epithelium may rapidly regenerate. Chronic bronchitis (CB), a form of COPD defined by persistent mucus hypersecretion and cough, is associated with poor quality of life, exacerbations, and lung function impairment. Symptom burden in CB is not correlated with the degree of impairment on pulmonary function testing. Bronchial Rheoplasty (BR) uses the RheOXTM system to deliver non-thermal pulsed electric fields to the airway epithelium and submucosa from the carina to approximately all 5th-order bronchi. Preliminary studies have demonstrated a reduction in airway goblet cell hyperplasia associated with improved symptoms. The RheOx system is an investigational device in the United States. Limited by federal (or United States) law to investigational use.
Fiducial Markers
In addition to medical applications, fiducial markers are widely employed in fields like computer vision, robotics, and geospatial mapping. In computer vision, they aid in object recognition and tracking, enabling machines to identify and interact with objects in the environment with high precision. Robotics systems use fiducial markers for navigation and positioning tasks, enhancing the accuracy and safety of robot movements. Geospatial mapping relies on these markers to precisely locate and align satellite imagery, aerial photographs, or ground-based measurements, facilitating the creation of detailed and accurate maps. Overall, fiducial markers are indispensable tools for achieving precision and accuracy in a wide range of scientific and technological endeavors.

Pulmonary Function Testing
Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT) is a comprehensive set of diagnostic assessments used to evaluate the functioning of the respiratory system. These tests provide valuable information about a person’s lung capacity, airflow, and overall respiratory health. Typically conducted by trained respiratory therapists or pulmonologists, PFTs are non-invasive and involve a series of breathing maneuvers that measure various lung parameters.
During a PFT, a patient is asked to breathe into a specialized machine called a spirometer, which records key measurements such as forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and the ratio of these values (FEV1/FVC). These measurements help diagnose and monitor a wide range of respiratory conditions, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, and restrictive lung disorders. PFTs can also assess how well a patient responds to bronchodilators, which are commonly used to treat asthma and COPD. Overall, Pulmonary Function Testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing respiratory diseases, tracking disease progression, and guiding treatment decisions, ultimately contributing to better respiratory health and an improved quality of life for patients.

Lung Cancer Diagnostics
Lung cancer diagnostics have evolved significantly in recent years, enabling earlier detection and more precise treatment strategies for this often-deadly disease. Diagnosing lung cancer typically involves a multi-step approach. It often starts with a thorough medical history and physical examination by a healthcare provider, including discussions about risk factors such as smoking history and exposure to environmental toxins. Imaging studies like chest X-rays or CT scans are often the next step, as they can reveal suspicious lung nodules or masses. These imaging techniques help in determining the size, location, and potential spread of the cancer within the lungs.
In addition to imaging, lung cancer diagnostics often involve obtaining tissue samples for further analysis. This can be done through minimally invasive procedures such as bronchoscopy, where a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the airways to collect samples of lung tissue or fluid. In cases where the cancer is not easily accessible via bronchoscopy, more invasive procedures like a CT-guided biopsy or a surgical biopsy may be necessary. Once tissue samples are obtained, they are analyzed in the laboratory to confirm the presence of cancer and determine the specific type and stage of lung cancer. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for guiding treatment decisions, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, or immunotherapy tailored to the individual patient’s condition. Advances in molecular testing and genetic profiling have further improved our ability to select the most effective treatment options for patients with lung cancer, emphasizing the importance of early and accurate diagnosis in improving outcomes.
Sleep Study / Sleep Apnea Test
A sleep study, also known as polysomnography, is a comprehensive diagnostic procedure conducted in a specialized sleep center or laboratory to evaluate and monitor an individual’s sleep patterns, quality, and overall sleep health. It is typically recommended for those who experience chronic sleep problems, such as insomnia, sleep apnea, narcolepsy, or restless leg syndrome, among others. During a sleep study, a trained sleep technician attaches various sensors to the patient’s body to record essential data while they sleep.
These sensors monitor a wide range of physiological factors, including brain activity, eye movement, muscle tone, heart rate, and respiratory patterns. Additionally, a sleep study may also measure oxygen levels, airflow, and body position. The collected data is then carefully analyzed by sleep specialists to diagnose sleep disorders and formulate appropriate treatment plans. Sleep studies play a crucial role in helping healthcare professionals gain insights into sleep-related issues, enabling them to provide tailored solutions to improve an individual’s sleep quality and overall well-being. Overall, sleep studies are essential tools in diagnosing and managing various sleep disorders, allowing individuals to achieve better sleep and lead healthier lives.

Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is a medical intervention used to provide a higher concentration of oxygen to individuals with breathing difficulties or conditions that result in low blood oxygen levels. This therapy is crucial in addressing various respiratory issues, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and pulmonary fibrosis, where the lungs struggle to extract sufficient oxygen from the air.
During oxygen therapy, a healthcare provider prescribes the appropriate oxygen flow rate, typically administered through a nasal cannula or a face mask. The goal is to increase the oxygen content in the patient’s bloodstream, ensuring that vital organs receive an adequate supply of oxygen. This helps alleviate symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, and confusion, ultimately improving the patient’s quality of life. Oxygen therapy can be administered in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, and even at home for patients with chronic respiratory conditions. It plays a pivotal role in managing and stabilizing the health of individuals with impaired lung function, allowing them to lead more active and fulfilling lives while mitigating the risk of complications associated with low oxygen levels.
Lung Cancer Tumor Ablation with Argon Plasma Coagulation
One of the notable advantages of Argon Plasma Coagulation for lung cancer treatment is its ability to target and treat tumors in a minimally invasive manner. Traditional surgical methods often involve more extensive procedures with greater risks and longer recovery times. APC can be performed through a bronchoscope, which is inserted through the mouth or nose, eliminating the need for surgical incisions. This results in reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery for patients. Furthermore, APC can be used to manage bleeding associated with tumors, making it particularly valuable in cases where bleeding is a complication. While it may not be suitable for all lung cancer cases, Argon Plasma Coagulation serves as a valuable adjunct to other treatments and helps improve the quality of life for individuals dealing with this challenging disease.

Bronchoscopic Lung Cryobiopsy
Bronchoscopic Lung Cryobiopsy is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure used to obtain lung tissue samples for the evaluation of various lung diseases, particularly those affecting the lung’s interstitial or parenchymal tissues. Unlike traditional surgical lung biopsies, which involve larger incisions and more invasive techniques, bronchoscopic cryobiopsy is performed through a bronchoscope, a flexible tube that can be inserted through the mouth or nose and into the lungs. This technique utilizes extreme cold, achieved through the use of a specialized cryoprobe, to freeze a small section of lung tissue. Once frozen, the tissue is then extracted and collected for examination under a microscope.
This procedure has gained popularity because it offers several advantages over an open surgical lung biopsy. It allows for a more precise and targeted approach to obtaining lung tissue samples, reducing the risk of complications associated with more invasive procedures. Additionally, bronchoscopic cryobiopsy often results in larger and more intact tissue specimens, which can improve the accuracy of diagnosing various lung conditions, including interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) such as pulmonary fibrosis. Despite its benefits, bronchoscopic lung cryobiopsy is not without risks, and it should be performed by experienced medical professionals in a controlled clinical setting to minimize potential complications. This technique plays a vital role in enhancing the diagnostic capabilities for respiratory diseases and improving patient care by providing valuable insights into the underlying causes of lung conditions.
ICU/Critical Care Management
Respiratory Failure
Respiratory failure is when your lungs can’t do their job properly, which is to get oxygen into your body and remove carbon dioxide waste. Respiratory failure in Bakersfield, CA, can happen for various reasons, like lung diseases or injuries. When your lungs fail, you might struggle to breathe or feel very tired. It’s a serious condition that needs medical attention right away, and doctors may use oxygen or machines to help you breathe until your lungs get better. So, it’s crucial to take care of your lungs and seek help if you are experiencing respiratory failure in Bakersfield, CA.
Non-invasive Ventilation
Non-invasive Ventilation (NIV) is a medical technique that provides respiratory support to individuals with breathing difficulties without the need for invasive procedures such as intubation or the insertion of a breathing tube into the windpipe. It involves the use of specialized devices, such as non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) machines or bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) machines, to deliver a controlled flow of air or oxygen through a mask or nasal prongs. NIV is a valuable tool in managing a range of respiratory conditions, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), congestive heart failure, neuromuscular disorders, and acute respiratory failure.
One of the key advantages of non-invasive ventilation is that it can improve oxygenation and assist with the removal of carbon dioxide from the body, thereby reducing the workload on the respiratory muscles. This can help alleviate symptoms like shortness of breath, improve overall comfort, and enhance the quality of life for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions. NIV is often used in hospital settings, but it can also be prescribed for home use in specific cases, allowing patients greater freedom and independence while maintaining their respiratory health. While NIV is generally considered a safer and less invasive option than invasive mechanical ventilation, it requires careful monitoring by healthcare professionals to ensure proper settings and patient comfort, as well as to prevent complications.
Tracheostomy Placement
Tracheostomy placement is a surgical procedure that involves creating a small opening, known as a stoma, in the front of the neck into the trachea (windpipe). This procedure is typically performed to establish an alternate and secure airway for patients who have difficulty breathing through their nose or mouth due to various medical conditions or emergencies. Tracheostomies are commonly utilized in critical care settings, such as intensive care units, to assist patients with severe respiratory problems, including those with prolonged mechanical ventilation needs or those who cannot maintain a clear airway on their own.
The placement of a tracheostomy tube is typically performed by a trained medical professional, such as a surgeon or an experienced specialist. The procedure involves making a small incision in the neck, followed by the insertion of a tube through the trachea to allow for a direct route for airflow. This surgical intervention offers several advantages, including improved oxygenation, reduced breathing work, and the ability to more effectively manage secretions. Tracheostomy placement may be temporary or permanent, depending on the patient’s underlying medical condition and recovery progress. While it can be a life-saving procedure, it also requires ongoing care and maintenance to prevent complications such as infection or blockage, making it essential for healthcare providers and caregivers to closely monitor and manage the patient’s tracheostomy site and tube.
Contact Us
Visit Us
5531 Business Park S, Suite 201a
Bakersfield, CA 93309
Hours
Mon-Fri: 9 am-5 pm
Sat-Sun: Closed